AI’s capacity to analyze massive quantities of data and make precise predictions has some wondering whether it eventually replace human doctors.
AI may enhance surgical results and minimize mistakes, but its limits prevent it from replacing humans.
In this blog post, we will explore the impacts of AI in the Job field of surgeons, take a look at some successful AI-Assisted surgeries, discuss the surgical procedure of AI, and finally take a deep look at the risks of AI in surgeries.

Will AI Replace Surgeons?
No, AI will not replace surgeons. However, AI will be a great help in the medical field, especially in early disease diagnosis. The use of robotics in surgeries can offer high accuracy rates, reducing the risk of long-term damage and disability in patients. AI will change the meaning of being a doctor and some tasks may change or go away entirely.
What Are The Impacts Of AI In The Job Sector Of Surgeon?
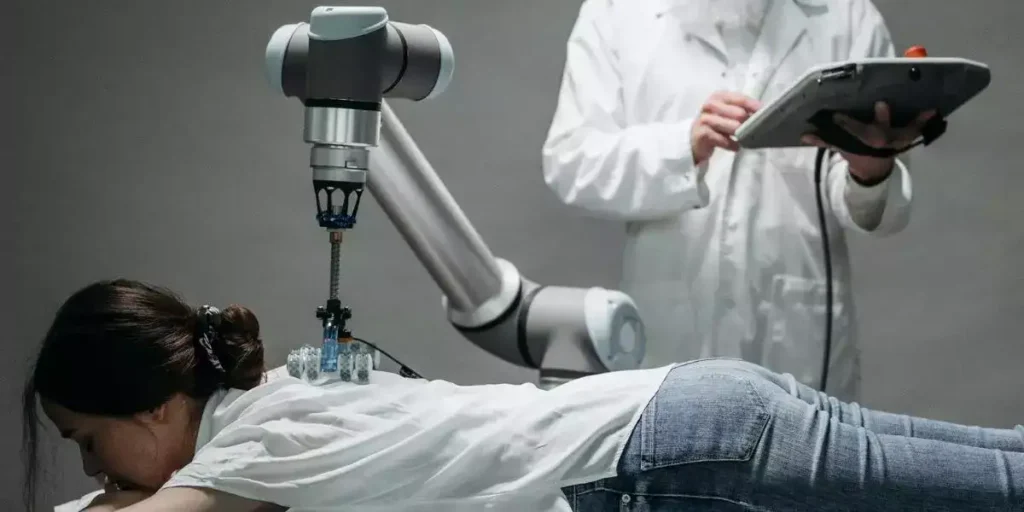

AI-assisted Surgery
AI-assisted surgery is one of the biggest effects of AI on surgeons. Minimally invasive AI-assisted surgery uses robots.
Surgeons can operate more precisely using real-time data and imagery from the AI system.
The robot can also perform a certain surgical technique without human assistance.
The da Vinci Surgical System is utilized in urology, gynecology, and other surgical disciplines.
A surgeon controls the da Vinci system from a console, and the robot performs the surgery precisely.
AI-assisted surgery has transformed surgery and decreased complications.
Medical Imaging and Diagnosis
AI has transformed medical imaging and diagnostics.
AI helps surgeons analyze and interpret medical pictures faster and more accurately.
AI can see minute changes in medical photos that humans cannot, improving diagnosis.
AI algorithms can better diagnose breast cancer in mammography than radiologists.
AI may identify brain tumors and other anomalies in MRI data that physicians may overlook.
AI can analyze medical pictures in real-time, giving doctors valuable information during operations.
Virtual Reality Training
Another impact of AI in the job sector of surgeons is the emergence of virtual reality training. Virtual reality (VR) technology is being used to train surgeons in a simulated environment.
VR training provides surgeons with a safe and controlled environment to practice surgical procedures without risking patient safety.
For example, VR technology can simulate a surgical procedure, and the surgeon can practice the procedure multiple times until they master it.
VR training has significantly improved the skills of surgeons and has made it possible to train more surgeons efficiently.
Increased accuracy and precision:
Another significant impact of AI in the job sector of surgeons is its ability to increase accuracy and precision during surgical procedures.
AI technology can analyze medical photos and data in real-time, helping surgeons spot issues and make better choices.
This eliminates mistakes and improves patient outcomes.
Minimally invasive operations employ the da Vinci Surgical technology, an AI-powered technology that improves accuracy and flexibility.
This technique allows difficult procedures using tiny incisions, lowering complications and recuperation time.
Reduced workload:
Another impact of AI in the job sector of surgeons is its ability to reduce the workload of surgeons.
Surgeons can automate data analysis, patient monitoring, and administrative procedures using AI.
This frees them up to make surgical decisions.
AI-powered technologies can analyze enormous patient records, discover trends, and give insights to improve diagnosis and therapy.
Surgeons can make better patient care choices with less labor.
Improved patient outcomes:
Predicting and avoiding problems using AI may enhance patient outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze medical history, vital signs, and lab findings to detect risks and problems.
Surgeons can avoid post-operative problems and improve patient recovery.
AI systems can anticipate post-operative infections and provide prevention tips. Patient outcomes and healthcare expenses may improve.
Potential job displacement:
AI may aid surgeons but possibly threaten their jobs. AI may be able to do certain surgical procedures as it advances. This may reduce surgical employment.
AI cannot replace surgeons’ competence. AI can handle mundane chores, but it can’t make surgical decisions. Thus, AI will not soon replace surgeons.
What Are Some Examples Of Successful AI-Assisted Surgeries?
Removal of brain tumors
The excision of brain tumors is one instance of a successful AI-assisted procedure. An AI algorithm was employed by surgeons at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Centre in Houston, Texas, to direct them while doing surgery.
In order to pinpoint the precise site of the tumor, the AI program examined live MRI images of the patient’s brain.
This made it possible for the surgeon to do more accurate tumor removal by more precise cutting.
The tumor was successfully removed during the procedure with little harm to the surrounding healthy tissue.
Surgery for Joint Replacement
Another effective use of AI in the medical industry is joint replacement surgery with AI assistance.
An AI program created by Johnson & Johnson helps doctors plan and carry out knee replacement surgeries.
The program builds a 3D model of the patient’s joint using information from CT images.
The model may then be used by the surgeon to plan where the joint replacement implant should be placed.
During the procedure, the AI program helps the surgeon by giving real-time input on the location and alignment of the implant.
As a consequence, the patient has improved outcomes from a more exact and precise joint replacement procedure.
Robotic Surgery
Another successful use of AI-assisted surgery is robotic surgery. With more accuracy and precision, minimally invasive procedures are being carried out by robots.
For instance, the da Vinci Surgical System is a robotic surgical tool that has been utilized for a variety of procedures, such as heart valve repairs, hysterectomies, and prostate cancer surgery.
The da Vinci technology enables surgeons to carry out intricate procedures with more control and accuracy, improving patient outcomes.
Retinal Surgery
Another illustration of how AI is changing medicine is in retinal surgery. An AI algorithm was utilized by surgeons at Moorfields Eye Hospital in London, England, to direct them while doing retinal surgery.
High-resolution retinal scans of the patient were analyzed by the algorithm, which gave the surgeon immediate input on the position and depth of the incision.
This enabled the surgeon to perform a successful procedure with little harm to the surrounding tissue by making more accurate incisions.
How Has AI Already Been Used In Surgical Procedures?
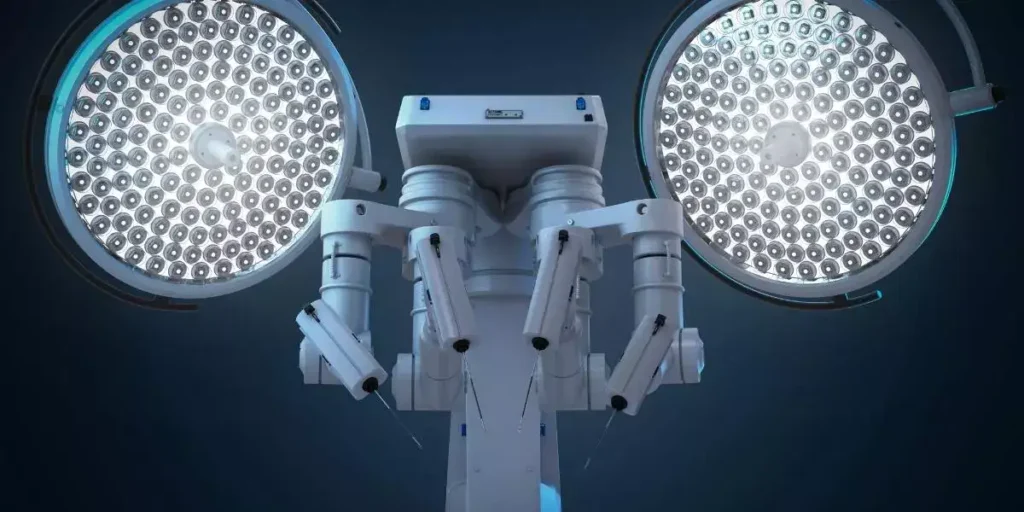

Preoperative Planning
AI aids surgical preoperative planning. MRI, CT, and X-ray pictures may be processed by AI algorithms to detect anatomical features, tumors, and operation strategies.
Surgeons may practice and perfect their techniques before surgery using AI.
AI can design the ideal location for joint replacements in orthopedic surgery. Surgeons can reduce problems like dislocation and infection by using AI to forecast them.
Robot-Assisted Surgery
AI is also used to assist with robot-assisted surgery. Robot-assisted surgery involves the use of robotic arms and instruments, controlled by a surgeon who sits at a console and manipulates the controls.
AI algorithms can help the robot interpret the surgeon’s movements, ensuring that the instruments move in a precise and controlled manner.
For example, in prostate surgery, AI can help the robot navigate the complex anatomy of the prostate, ensuring that the cancerous tissue is removed while preserving the nerves that control the bladder and sexual function.
AI can also help the robot compensate for any movements or tremors in the surgeon’s hand, ensuring that the instruments move smoothly and accurately.
Intraoperative Observation
AI may aid intraoperative monitoring. AI algorithms can assess real-time sensor data to inform the surgeon of the patient’s vital signs and other physiological parameters.
AI may alert the surgeon to changes in the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels during cardiac surgery. AI may also help surgeons anticipate bleeding and arrhythmias.
Postoperative Care
Finally, postoperative care may be aided by AI. In order to help identify patients who could be at risk of problems or readmission to the hospital, AI algorithms can analyse data from electronic medical records, monitoring devices, and other sources.
In general surgery, for instance, AI may assist in identifying patients who may be at risk of contracting infections like sepsis or surgical site infections.
AI may also assist in tracking the patient’s recovery to make sure they are improving and getting the right treatment.
What Skills Should Learn By Surgeon To Ensure The Optimal Uses Of AI?
Medical Imaging
Modern medicine relies on medical imaging to diagnose and treat many diseases. AI can detect illnesses like lung cancer in this region. Surgeons must know how to analyse and code hundreds of photos.
They must also understand X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. This may help them examine photographs and choose the best treatment.
Machine Learning
Machine learning teaches computers from data. Machine learning algorithms can examine virtual reality simulator datasets to improve psychomotor performance.
Surgeons must understand these strategies to stay up with training and evaluation.
They must also understand reinforcement, unsupervised, and supervised machine learning techniques.
This knowledge may help them improve patient outcomes with these devices.
AI Applications in Healthcare
Automation of regular activities as well as illness prediction and prevention with AI have the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry.
In order to guarantee that best practices are consistently used in healthcare, surgeons need to be knowledgeable about the many types of AI currently being researched.
This includes being aware of how AI may be used to better effectively arrange the rotation of medical personnel by matching the skills of healthcare professionals to certain jobs.
The ethical challenges regarding the use of AI in healthcare, such as those involving prejudice and privacy, should also be known to them.
Familiarity with AI Tools
Surgeons should be knowledgeable about the different frameworks and libraries used to create AI applications in order to be competent in AI.
TensorFlow, SciPy, NumPy, Scikit-Learn, Apache Spark, PyTorch, and more programs are examples of such tools.
Additionally, they must to be knowledgeable in data visualization programs like Tableau and Power BI as well as programming languages like Python and R.
They will be able to produce high-quality code more quickly with the aid of this expertise, which will speed up the development and deployment of AI applications.
Virtual Reality and Mobile Apps
Mobile applications, virtual and augmented reality, both have the potential to completely change how surgeons interact and train.
These technologies may be utilized to give interactive training modules, replicate surgical procedures, and even enable remote consultations.
Surgeons need to be knowledgeable about these technologies and how to use them in healthcare.
They should be aware of these products’ possible drawbacks, such as problems with user acceptability and data security.
Computer Systems and Hardware
To imitate human cognitive processes like learning, reasoning, and self-correction, artificial intelligence needs highly developed computer hardware and software.
The technology and software required to build artificial intelligence systems should be familiar to surgeons.
This requires an understanding of distributed systems, parallel computing, and computer architecture.
They should also be knowledgeable about the various hardware configurations, like GPUs and TPUs, that are utilized to speed up AI tasks.
Their ability to create and implement AI applications more effectively will improve patient outcomes and save healthcare expenditures.
What Are The Potential Risks Of Using AI In Surgery?
Technical Errors:
One of the most significant risks of using AI in surgery is technical errors. AI algorithms rely on accurate data to make informed decisions.
If the data input into the system is incorrect, the AI algorithm can make incorrect decisions, leading to technical errors.
These errors can result in complications during surgery, such as incorrect incisions, excessive bleeding, and even death.
For example, a surgeon may rely on an AI system to guide them during surgery, but if the system malfunctions or is hacked, it could lead to disastrous outcomes.
Overreliance on Technology:
Another potential risk of using AI in surgery is an overreliance on technology. Surgeons may become too dependent on AI algorithms and stop relying on their skills and expertise.
This overreliance on technology could result in surgeons becoming less skilled over time and relying on the AI algorithm to make all critical decisions.
Lack of Understanding:
AI algorithms can be complex and difficult to understand, which could result in a lack of understanding by surgeons.
If surgeons do not understand how the AI algorithm works, they may not be able to identify potential errors or misinterpretations made by the algorithm.
This lack of understanding could lead to mistakes and errors during surgery.
Data Bias:
AI algorithms rely on data input to make informed decisions. However, if the data is biased, the AI algorithm will be biased as well.
For example, if an AI algorithm is trained on data that only includes male patients, it may not be as effective when used on female patients.
This data bias could lead to incorrect decisions during surgery, resulting in complications and adverse outcomes.
Legal and Ethical Concerns:
The use of AI in surgery raises legal and ethical concerns. If something goes wrong during surgery, who is responsible? The surgeon or the AI algorithm?
Additionally, there are concerns about the privacy and security of patient data used to train AI algorithms.
Surgeons must be aware of these legal and ethical concerns and ensure they are using AI in a responsible and ethical manner.
FAQs
Can AI Perform Surgical Procedures Better Than Human Surgeons?
AI has the potential to perform certain surgical procedures more accurately and efficiently than human surgeons, but there are still limitations to what AI can currently do. Surgeons possess critical thinking skills, judgment, and intuition that AI lacks.
What Role Does AI Currently Play In Surgery?
AI is currently used in surgery for tasks such as preoperative planning, image-guided surgery, and robotic surgery. AI can also assist surgeons in decision-making during surgery, but the ultimate responsibility for the procedure lies with the surgeon.
Can AI Perform Surgeries Without Human Intervention?
At present, AI cannot perform surgeries without human intervention. AI can assist surgeons during surgery, but the final decision-making and physical manipulation of surgical instruments must be done by the surgeon.
Will AI Completely Replace Human Surgeons In The Future?
It is unlikely that AI will completely replace human surgeons in the future. While AI can assist surgeons and improve surgical outcomes, the decision-making and physical manipulation of surgical instruments will likely remain in the hands of human surgeons.
How Can Surgeons Prepare For The Integration Of AI Into The Surgery?
Surgeons can prepare for the integration of AI into surgery by staying up-to-date on advances in AI technology and training, and by collaborating with AI experts and incorporating AI into their surgical practices. Surgeons can also be mindful of the limitations of AI and continue to prioritize critical thinking and judgment in their decision-making.
Conclusion
The question of whether AI will replace surgeons is a complex one. While AI technology has the potential to improve surgical outcomes and reduce errors, it cannot fully replace the skill and expertise of a human surgeon.
Surgeons should embrace the potential benefits of AI while continuing to hone their own abilities and knowledge.
The future of surgery is likely to involve a partnership between human surgeons and AI technology, rather than one replacing the other.