One such industry is publishing, where there is growing concern about whether AI will replace editors. While AI can certainly assist editors in their work, it does have limitations.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the impacts of AI on the Editor job industry, how editors prepare for the rise of AI, examples of some AI editing tools, and the risks of using AI.

Will AI Replace Editors?
No, AI is not yet advanced enough to replace human video editing editors fully.
While AI can assist in some tasks, it lacks creativity and the human touch needed for high-quality video editing.
Canva recently announced a suite of AI tools for generating new images and automatically editing videos, but it’s still not a complete replacement for human editors.
What Are The Impacts Of AI On The Job Market For Editors?
Automation of Editing Tasks
One of the most significant impacts of AI on the job market for editors is the automation of editing tasks.
AI can be used to automatically proofread documents, check grammar, punctuation, and spelling, and even suggest changes to sentence structure.
This has the potential to reduce the amount of time editors spend on menial tasks and allow them to focus on more complex editing tasks.
For example, AI-powered editing software like Grammarly can detect grammatical errors and suggest corrections, saving editors time.
Increased Competition
Another impact of AI on the job market for editors is increased competition. As more editing tasks become automated, it becomes easier for non-professionals to edit their work.
This means that there is less demand for professional editors, and those who remain in the industry face more competition from non-professionals.
In addition, AI-powered editing software can be used by non-professionals, further increasing competition.
New Opportunities
While AI may reduce demand for some traditional editing tasks, it also creates new opportunities for editors.
For example, as more businesses adopt AI technology, there will be an increased demand for editors who can write content for AI systems.
Additionally, AI can be used to analyze large amounts of data, which can help editors identify trends and patterns in the content they are editing. This means editors with AI technology experience will be in high demand.
Adaptation and Re-skilling
To remain competitive in the job market, editors must be willing to adapt and re-skill.
As AI continues to advance, traditional editing tasks may become automated, and editors must be able to provide value in new ways.
This may involve learning new skills, such as writing content for AI systems or analyzing data using AI technology.
It may also involve learning how to work with AI-powered editing software to provide more efficient editing services.
How Can Editors Prepare For The Rise Of AI In The Industry?

Familiarize yourself with AI technology.
It is critical to have a fundamental grasp of what AI is and how it works in order to prepare for the emergence of AI in the industry.
AI technology is used to automate processes that formerly required human intellect, such as language translation, picture recognition, and decision-making.
Machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision are examples of AI. Understanding these technologies will allow you to find possible AI uses in your editing workflow and remain up to speed on the newest advances.
Identify areas where AI can improve your workflow.
AI’s most significant advantage is its capacity to automate repetitive and time-consuming jobs.
As an editor, you may discover areas in your workflow where AI can be utilized to improve productivity and optimize operations.
AI, for example, may be used to automate activities like proofreading, grammar checking, and plagiarism detection, freeing up your time to focus on higher-level editing.
Evaluate AI tools and software.
Once you’ve identified areas where AI can help your workflow, you should evaluate the available tools and software.
Several AI-powered editing tools are on the market, ranging from basic grammar checkers to more complex programs that employ machine learning algorithms to generate content ideas and comments.
Consider accuracy, convenience of use, and cost while assessing these instruments.
Implement AI tools into your workflow.
After evaluating the available AI tools, it’s time to implement them into your workflow. This may involve integrating the tools into your existing editing software or using them as standalone applications.
When implementing AI tools, it’s important to train yourself and your team on how to use them effectively to achieve the desired results.
Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of AI in your workflow.
As with any new technology, it’s critical to track and assess the effectiveness of AI in your workflow.
This includes measuring productivity, accuracy, and user happiness to see if the AI technologies are achieving the anticipated results.
If the tools fail to match your expectations, you may need to reconsider your implementation plan or look into alternate options.
What Are Some Examples Of Successful AI-Powered Editing Tools?
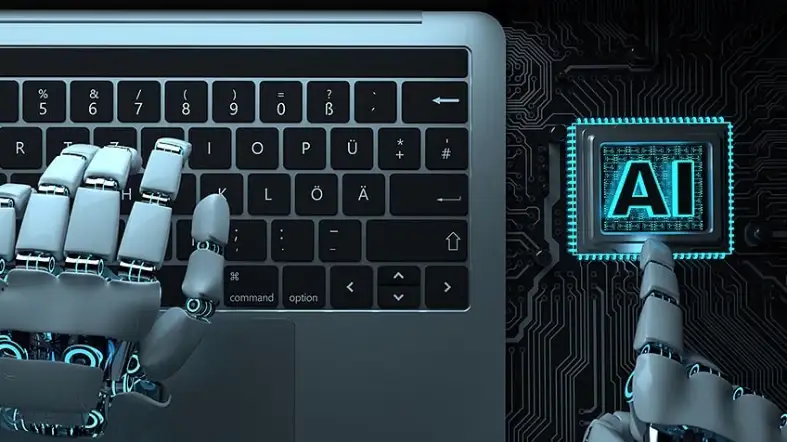
Grammarly
Grammarly is a well-known AI-powered editing tool that assists authors and editors in proofreading their work.
It employs powerful algorithms to detect and repair grammar, spelling, punctuation, and stylistic issues.
The program gives authors specific feedback on sentence structure, word choice, and writing style, helping them to improve their writing abilities and generate error-free material.
Grammarly also includes a plagiarism checker to assist authors in confirming that their writing is unique and not plagiarized from other sources.
Hemingway Editor
Hemingway Editor is another AI-powered editing tool that helps writers to improve their writing style.
It analyzes the readability of text by highlighting complex sentences, passive voice, and unnecessary adverbs.
The tool provides suggestions on simplifying the text and making it more engaging for readers.
Hemingway Editor also identifies instances of repetition and offers suggestions on how to vary sentence structure to avoid monotony.
ProWritingAid
ProWritingAid is an artificial intelligence-powered editing application that gives detailed comments on grammar, spelling, style, and organization.
It provides real-time feedback on sentence structure, word choice, and writing style. The program also delivers thorough data on text readability, including statistics on sentence length, passive voice usage, and adverb density.
ProWritingAid also includes a plagiarism checker to help authors guarantee that their writing is unique and not plagiarized from other sources.
AutoCrit
AutoCrit is an AI-powered editing tool that focuses on fiction writing. It analyzes the manuscript and provides suggestions on how to improve the plot, pacing, characterization, and dialogue.
The tool also identifies instances of overused words, adverbs, and passive voice, providing suggestions on how to make the text more engaging for readers.
AutoCrit also offers a feature that compares the manuscript with published works in the same genre, providing insights into how to improve the manuscript to meet industry standards.
Wordtune
Wordtune is an AI-powered editing tool that helps writers to improve the tone and style of their writing.
It analyzes the text and provides suggestions on how to rephrase sentences to convey the desired tone and style.
The tool also offers options to simplify or expand sentences and provides suggestions on how to vary sentence structure to make the text more engaging for readers.
Wordtune is particularly useful for email communication, as it helps writers to convey the right tone and message in a concise and clear manner.
What Are The Potential Risks Of Using AI To Replace Editors?

Lack of nuance and context
The absence of depth and context in AI-generated articles is one of the most serious hazards of utilizing AI to replace editors.
While AI can generate articles quickly and efficiently, it may overlook important details that only a human editor can detect.
For example, AI may be unable to differentiate between a politician’s opinion on a certain topic and their public relations spin.
On the other hand, a human editor would be able to detect the discrepancy and guarantee that the piece correctly reflects the politician’s beliefs.
Bias and stereotypes
Another potential risk of using AI to replace editors is the perpetuation of bias and stereotypes in news reporting.
AI algorithms are only as accurate as the data on which they are trained. If the data used to train the AI contains biases or stereotypes, those biases will be reflected in the output.
For example, suppose the AI is trained on news articles that disproportionately focus on crime in low-income neighborhoods.
In that case, it may reinforce stereotypes about those communities, even if that was not the intent.
Limited creativity and originality
AI-generated articles may lack creativity and originality. AI is programmed to follow specific rules and templates, which may result in a lack of originality in the content it produces.
In contrast, human editors can bring their creativity and unique perspectives to the table, resulting in more engaging and interesting articles.
Lack of accountability
The lack of responsibility is another possible downside of utilizing AI to replace editors.
Determining who is to blame may be challenging if an AI-generated piece has errors or inaccuracies. In contrast, if a human editor makes a mistake, they may be held accountable and corrected.
Loss of jobs
Finally, the use of artificial intelligence to replace human editors may result in job losses. While AI may be more efficient and cost-effective, it cannot replace the value provided by human editors.
Human editors may provide a personal touch, identify errors that AI may overlook, and contribute a degree of inventiveness and critical thinking that AI cannot match. The loss of these employees might have serious economic and societal ramifications.
FAQs
What Is The Current State Of AI In The Field Of Editing?
AI is beginning to replace editors at the entry-level, particularly in duties like proofreading and copy editing.
However, there is still much debate about whether AI can completely replace the human touch in editing, especially for higher-level tasks like structural editing and developmental editing.
What Are Some Examples Of AI Writing Tools That Exist Today?
Many AI writing tools are available today, including Writesonic, Sudowrite, Copy.ai, and PicsArt AI Writer.
These tools can generate high-quality copy for a variety of situations and languages, from marketing content to LinkedIn headlines and Instagram captions.
Can AI Replace Human Copywriters?
While some experts believe that AI will eventually replace human copywriters in certain situations, this is still a hotly debated topic.
Some argue that AI will never fully replicate the nuances of human writing and creativity, while others believe AI will eventually outperform human writers in certain tasks.
What Are Some Potential Benefits Of Using AI In Editing?
One potential benefit of using AI in editing is that it could speed up the editing process, particularly for tasks like proofreading and copy editing.
Additionally, AI could help catch errors and inconsistencies that a human editor might miss, improving the overall quality of the final product.
Can AI Ever Fully Replace Human Editors?
While it’s difficult to predict the future of AI in editing, most experts agree that AI is unlikely to replace human editors anytime soon fully.
While AI may eventually be able to handle certain tasks like proofreading and copy editing, it will likely struggle to replicate the creativity and intuition of human editors in more complex tasks.
Conclusion
Although artificial intelligence technology is developing at an astounding rate, it is unlikely to replace human editors in the near future completely.
Editors bring a critical eye and a depth of expertise that AI cannot match. While AI can be a valuable tool for editing and proofreading, it falls short of a human editor’s creativity and ability to make complex judgment calls.
Therefore, it is obvious that the human touch will continue to be an essential part of the editorial process even though the editor’s role may change.